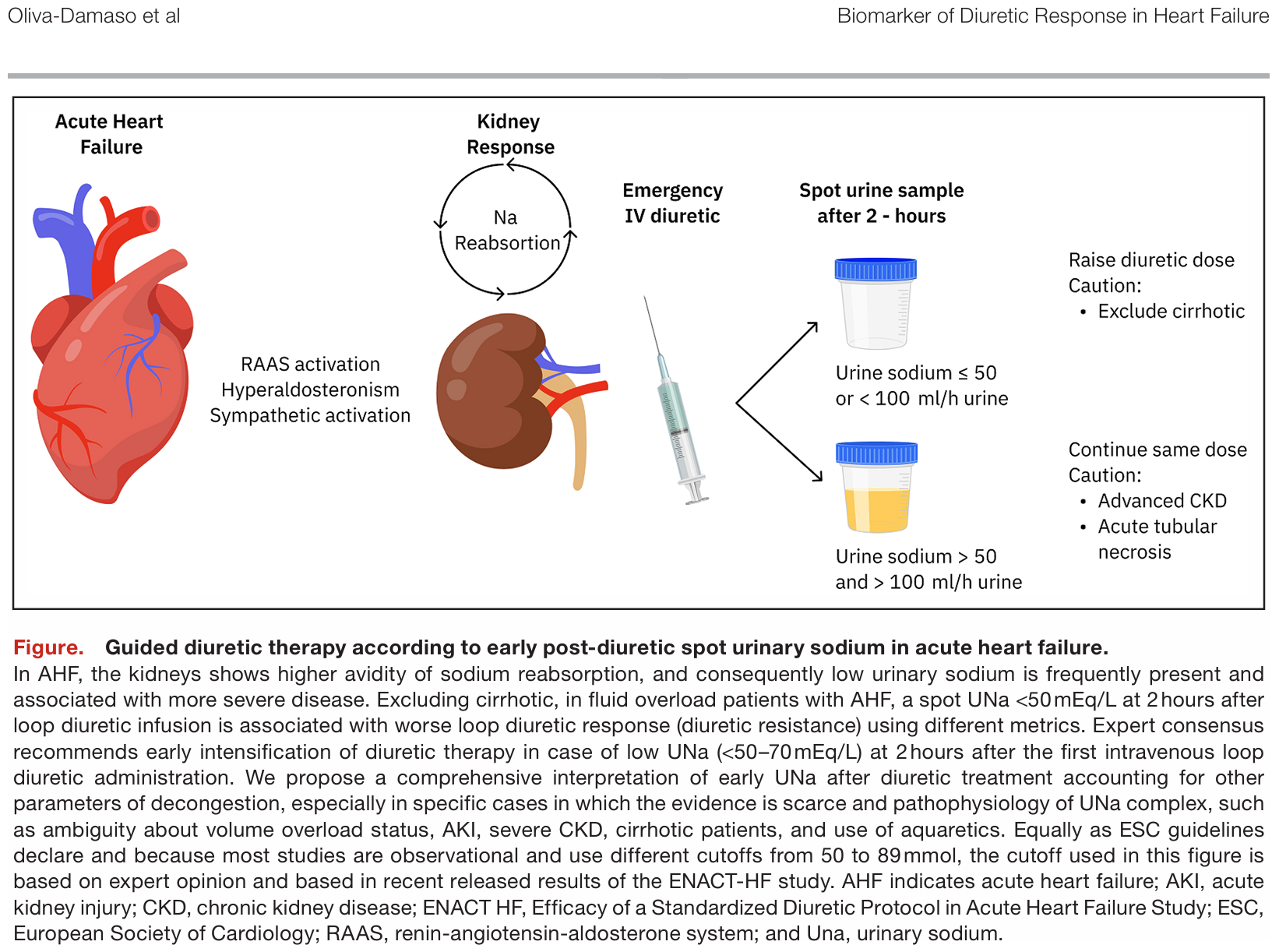
Spot Urinary Sodium as a Biomarker of Diuretic Response in Acute Heart Failure
Urinary sodium (UNa) measured in a timed urine collection sample or spot urine measurement has emerged as a promising biomarker of diuretic response in patients with acute HF (AHF). European Society of Cardiology (ESC) HF guidelines recommends an early evaluation of loop diuretic treatment response with a spot UNa analysis in patients with AHF after 2 hours of decongestive therapy initiation. According to this statement, a patient with fluid overload presents a UNa <50 to 70 mEq/L in a urine spot sample after a 2- hour diuretic administration or an hourly urine output <100 to 150 mL during the first 6 hours, generally identifies those with an insufficient diuretic response, and recommends doubling the intravenous loop diuretic dose or adding another diuretic to obtain incremental diuresis/natriuresis. This proactive approach for AHF management is based on findings from observational studies and expert opinion.
Thanks to the authors.